Pregnancy Week By Week: Importance, Stages, And Symptoms
Pregnancy, typically lasting around 40 weeks, is measured from the first day of a woman’s last menstrual period (LMP). It’s important to understand pregnancy week by week to track fetal development and manage pregnancy symptoms week by week. There are three trimesters of pregnancy: the first (weeks 1-12), the second (weeks 13-28), and the third (weeks 29-40). Each trimester has distinct developmental milestones and symptoms.
During the first trimester, common symptoms include fatigue, nausea, and tender breasts. By the second trimester, many early symptoms subside, and the baby grows rapidly. The third trimester involves significant weight gain and the baby’s final development, preparing for birth.
Prenatal care, or antenatal care, is important throughout the pregnancy timeline for early detection of complications, monitoring fetal growth, and ensuring the mother’s health. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle by eating a balanced diet, staying active, managing stress, and avoiding harmful substances is essential for mother and baby’s health.

How Many Weeks is a Pregnancy?
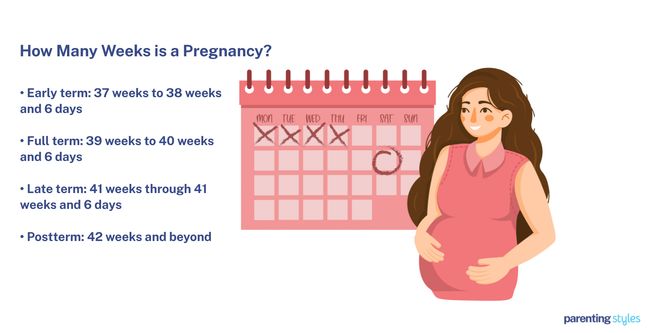
Pregnancy typically lasts around 40 weeks or 280 days, measured from the first day of a woman’s last menstrual period (LMP) to the delivery date. In the past, births between 37 and 42 weeks were considered full-term, indicating the fetus was mature and ready for birth. However, “term pregnancy” was redefined as the following in a joint announcement by The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) and the Society for Maternal Fetal Medicine (SMFM).
- Early term: 37 weeks to 38 weeks and 6 days
- Full term: 39 weeks to 40 weeks and 6 days
- Late term: 41 weeks through 41 weeks and 6 days
- Postterm: 42 weeks and beyond
The redefinition of “term pregnancy” resulted from a 2012 meeting of experts from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, the American Academy of Pediatrics, the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine, the March of Dimes, and the World Health Organization (WHO).
Data showed that delivery risks were lowest, and babies fared best when born full-term, between 39 weeks and 40 weeks and 6 days. However, in the paper “Defining “Term” Pregnancy Recommendations From the Defining “Term” Pregnancy Workgroup,” published in Jama, Catherine Y. Spong, MD emphasized that giving birth between 37 weeks 0 days and 38 weeks 6 days is appropriate if the delivery is medically indicated, or if the onset of labor or rupture of membranes is spontaneous.
What is the Importance of Understanding Pregnancy Week by Week?
Understanding pregnancy week-by-week is important for tracking the baby’s growth and monitoring the mother’s health. Knowing the pregnancy timeline allows doctors to follow fetal development, schedule essential prenatal screening, and estimate the pregnancy’s due date.

How are Pregnancy Weeks Calculated?
Pregnancy weeks, called the gestational age, are calculated in seven-day increments from the first day of a woman’s last menstrual period (LMP).
The first date of pregnancy differs from the date of conception, which often occurs 2 weeks later.
The most accurate method for estimating pregnancy weeks is obtaining a sonography, according to Spong at the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. Women with irregular or uncertain menstrual cycles are recommended to have an early sonography to accurately date their pregnancy. Others with regular menstrual cycles wait until 18 to 20 weeks for sonography, which serves as an anatomical survey of the fetus to determine an accurate gestational age.
What is the Purpose of a Pregnancy Calendar?
A pregnancy calendar aims to track your pregnancy progress at a glance, offering a visual and comprehensive overview of your journey from conception to birth. This tool consolidates various aspects of pregnancy into an easy-to-understand format, allowing expectant parents to visualize the timeline, monitor fetal growth, track symptoms, anticipate changes, plan ahead, celebrate milestones, and countdown to the estimated due date.
A pregnancy calendar consolidates all this information into one accessible format, serving as a roadmap for the entire pregnancy journey. Expectant mothers easily stay informed and engaged with a single glance.

How To Calculate When Is Your Due Date?
Your Estimated Due Date (EDD) is around 40 weeks, or 280 days, from your last menstrual period (LMP). Add 280 to your LMP to obtain your due date. A pregnancy due date calculator helps you calculate your due date so you can track your pregnancy’s weekly progress.
What are the Stages of Pregnancy?
There are three pregnancy stages, called the first, second, and third trimesters. Each trimester lasts roughly three months. Pregnancy trimesters are defined as the following by the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development.
- The first trimester weeks are weeks 1 to 12
- The second trimester weeks are weeks 13 to 28
- The third trimester weeks are weeks 29 to 40

First Trimester of Pregnancy
The first trimester lasts roughly three months, from week 1 to week 12. Major first-trimester pregnancy symptoms include fatigue, tender breasts, nausea, and poor appetite, according to the 2001 study “Symptoms across pregnancy in relation to psychosocial and biomedical factors” conducted by the Departments of Psychology and Obstetrics and Gynecology at Uppsala University in Sweden. Many women occasionally experience headaches, stomach pain, dizziness, and constipation.
It’s important to note that symptoms are not universal. Every pregnancy is unique, and the timing and intensity of symptoms vary from person to person. Some women experience symptoms earlier or later than described, while others do not experience symptoms at all.
How long is the first trimester? The first trimester lasts around three months.
When does the first trimester end? The first trimester ends at week 12.
Week 1 of Pregnancy
Week 1 of pregnancy marks the beginning of gestation, even though conception has not happened yet. The thickened uterine lining (endometrium) sheds in this week, resulting in a menstrual period.
Several follicles (fluid-filled sacs containing eggs) begin to mature in the ovaries in week 1. During ovulation, one mature egg is released. Ovulation occurs around day 14 in a 28-day menstrual cycle. 1 week pregnant symptoms include menstrual symptoms, such as menstrual bleeding, cramping, bloating, and mood changes.
Week 2 of Pregnancy
Week 2 of pregnancy is still not an official pregnancy. In the medical context, pregnancy begins at implantation, which happens around week 3. However, pregnancy is dated from the first day of the LMP. Therefore, week 2 is the week leading up to ovulation. Your body is preparing for ovulation and the possibility of conception toward the end of this week.
Eggs mature within fluid-filled sacs called follicles in the ovaries in week 2 of pregnancy. Your hormones, including estrogen and progesterone, rise, and the lining of your uterus (endometrium) thickens in preparation to receive and nourish a fertilized egg. Toward the end of week 2, a mature egg is released from a follicle, marking the peak fertility period. If unprotected sex occurs around ovulation, the egg can be fertilized by sperm. 2 weeks pregnant symptoms include subtle changes in the body, such as slippery cervical mucus, mild cramping, increased sex drive (libido), heightened sense of smell, and tender breasts. These changes prepare your body for ovulation.
Week 3 of Pregnancy
Week 3 of pregnancy marks a significant milestone: conception. Women are 3 weeks pregnant when the sperm fertilizes the egg in the fallopian tube, forming a single-celled zygote. The zygote begins to rapidly divide, forming a cluster of cells called a blastocyst. The blastocyst travels down the fallopian tube and arrives in the uterus. The blastocyst burrows into the lining of the uterus (endometrium), establishing a connection that nourishes and supports the developing embryo. This process is called implantation.
While implantation may occur around week 3, most women do not experience noticeable pregnancy symptoms until several weeks later. The hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is produced upon successful implantation and is detected in pregnancy tests.
In week 3, the hCG levels are still too low to be detected by a home pregnancy test. 3 weeks pregnant symptoms for some women include implantation bleeding, mild cramping, and breast tenderness. Many women do not notice any changes during this early pregnancy.
Week 4 of Pregnancy
Week 4 of pregnancy is when the first pregnancy symptom emerges for the expectant mother. The blastocyst implanted in the uterine wall during week 3 forms two layers in week 4: the epiblast, which becomes the embryo, and the hypoblast, which forms the yolk sac.
The amniotic sac, filled with amniotic fluid, starts forming around the embryo, providing protection and cushioning. The yolk sac develops to provide early nourishment for the embryo until the placenta takes over. The placenta, the organ responsible for exchanging nutrients and waste between the mother and the developing baby, begins to form.
Most 4 weeks pregnant women realize they are pregnant because their period hasn’t arrived. 4 weeks pregnant symptoms start to appear in some women, including fatigue, nausea (morning sickness), frequent urination, mood swings, food cravings or aversions, and a heightened sense of smell.
However, not all women experience these symptoms. If you suspect you’re pregnant, take a home pregnancy test that detects the hCG hormone in your urine.
If you haven’t already, schedule your first prenatal appointment with your healthcare provider. They will confirm your pregnancy, discuss your medical history, and provide guidance for a healthy pregnancy.
Week 5 of Pregnancy
Week 5 of pregnancy is a time of rapid development for the embryo. The embryo is now the size of a grain of rice and has three distinct layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. At five weeks pregnant, the neural tube, which eventually develops into the brain and spinal cord, starts to form. This is a crucial period for neural development.
Early pregnancy symptoms tend to intensify this week. Many 5 weeks pregnant women experience pregnancy symptoms. The 5 most commonly reported 5 weeks pregnant symptoms are fatigue, nausea, frequent urination, appetite changes, and urgency in urination.
Home pregnancy tests now reliably detect the hCG hormone in your urine. This is often the week when women schedule their first prenatal visit. The doctor will confirm the pregnancy, perform a physical exam, and order blood tests in the initial prenatal care visit.
Week 6 of Pregnancy
Week 6 of pregnancy is exciting as your baby’s development kicks into high gear. The embryo is now about the size of a sweet pea and starts to look more human, with limb buds beginning to form. Facial features, like the eyes, nose, and ears, are beginning to develop. Inside, your baby’s organs, such as the heart and lungs, start to develop and function.
The neural tube, which eventually develops into the brain and spinal cord, is closing up. It’s a crucial time for your baby’s development, so ensure you care for yourself and follow your prenatal care plan. The most common 6 weeks pregnant symptoms include fatigue, nausea, and urgency to urinate. You notice changes in your appetite or food preferences and frequent urination due to hormonal changes. Listen to your body, rest when needed, and stay hydrated.
Week 7 of Pregnancy
During Week 7 of pregnancy, anticipation builds as your baby has grown large enough to be visible on an ultrasound. If you have a scheduled prenatal appointment this week, you will likely see your baby for the first time. This moment marks a significant milestone for many expectant mothers, making the pregnancy feel tangibly real. The image on the screen, however small, often provides a special emotional connection, transforming abstract knowledge into a visible reality.
Your baby is now the size of a blueberry and is growing rapidly. Major organs, such as the brain, heart, and gastrointestinal (GI) tract, are developing rapidly. Tiny hand and foot plates start to appear. The umbilical cord, the lifeline that connects you and your baby, is becoming more defined. It’s vital that you get enough nutrients to support your baby’s growth.
You start feeling even more tired than usual at 7 weeks pregnant. Nausea and vomiting are among the more pronounced 7 weeks pregnant symptoms. Insomnia, forgetfulness, and heartburn are also common symptoms.
Week 8 of Pregnancy
Week 8 of pregnancy marks the end of the embryonic period and the beginning of the fetal period. Your baby, now the size of a kidney bean, looks more and more like a tiny human. The facial features are becoming more distinct, with the nose and upper lip taking shape. The arms and legs are getting longer, and the fingers and toes are starting to form.
You continue to experience symptoms like fatigue, nausea, and breast tenderness. You start experiencing heartburn, indigestion, and headaches. Staying hydrated and eating small, frequent meals is important to manage these 8 weeks pregnant symptoms.
As for developmental milestones, week 8 of pregnancy marks the beginning of bone development in your baby. The tiny bones are starting to form, replacing the cartilage that was there before. The muscles develop, allowing your baby to start making small movements. The ears are forming, and the eyelids are beginning to cover the eyes.
Week 9 of Pregnancy
Week 9 of pregnancy brings about significant changes in your baby’s development. Now the size of a grape, your baby’s facial features are becoming even more defined, with the eyes, nose, mouth, and ears all taking shape. The arms and legs are growing longer, and the elbows and knees are starting to bend. The fingers and toes are growing longer and starting to separate.
You notice some new symptoms, like dizziness or lightheadedness. Other 9 weeks pregnant symptoms include skin changes, like acne or pigmentation. Remember to take care of your skin and stay hydrated.
For developmental milestones, week 9 of pregnancy marks the beginning of the development of your baby’s reproductive organs. The ovaries or testicles are starting to form, although it’s still too early to determine the sex of your baby. The kidneys are starting to function, and the liver is starting to produce blood cells.
Week 10 of Pregnancy
Week 10 of pregnancy is another exciting milestone. Your baby, now the size of a prune, is growing rapidly, and its organs are maturing. The head is still large in proportion to the body, but the arms and legs are getting longer, and the fingers and toes are well-defined. The external genitalia are starting to develop.
You start noticing changes in your body, like a growing belly and a widening waistline. 10 weeks pregnant symptoms peak in intensity and feel the worst. It’s important to embrace these changes and wear comfortable clothing.
As for developmental milestones, week 10 of pregnancy marks the end of the embryonic period and the beginning of the fetal period. Your baby is now officially a fetus, and its major organs have been formed. The brain is developing rapidly, and the nerve cells are starting to connect. The muscles continue developing, allowing your baby to start making more coordinated movements.
Week 11 of Pregnancy
During week 11 of pregnancy, your baby grows rapidly and looks more like a miniature human. Their head is still relatively large compared to the rest of their body, but their arms and legs are lengthening, and their fingers and toes are no longer webbed. Inside, their organs are maturing, and their intestines move from the umbilical cord to their abdomen.
You are starting to feel a little more energetic as your pregnancy hormones start to level out. Some women even notice a decrease in nausea and vomiting. However, other symptoms like fatigue, breast tenderness, and frequent urination continue. 11 weeks pregnant symptoms include fatigue, breast tenderness, frequent urination, constipation, heartburn, and mood swings. You experience skin changes, such as acne or stretch marks. Remember to stay hydrated, eat a healthy diet, and get plenty of rest.
At 11 weeks pregnant, your baby’s development is focused on refining its features and bodily systems. Their fingernails and toenails are starting to form, and their external genitalia are beginning to develop. Their diaphragm is forming, which is essential for breathing after birth. If you have an ultrasound this week, you will likely see your baby moving around.
Week 12 of Pregnancy
Week 12 of pregnancy marks the end of the first trimester. Your baby, now about the size of a lime, is starting to move more, although you probably don’t feel it yet. Their reflexes are developing, and they suck their thumb. Their vocal cords start forming, and their kidneys produce urine.
You feel more like yourself this week, with less nausea and fatigue. Your energy levels return, and you show a small baby bump. Common 12 weeks pregnant symptoms include fatigue, breast tenderness, frequent urination, constipation, heartburn, and mood swings. You experience some leg cramps or varicose veins. If you haven’t already, this is a good time to consider maternity clothes.
Regarding developmental milestones, your baby’s bones are hardening, and their fingernails and toenails continue to grow. Their intestines start producing meconium, the dark, sticky substance that is their first bowel movement after birth. Their thyroid gland is starting to produce hormones important for growth and development.
Second Trimester of Pregnancy
The second trimester spans from week 13 to week 28. The second trimester is often considered the most comfortable period for expectant mothers. Second-trimester pregnancy symptoms are less severe as many early pregnancy symptoms subside, such as morning sickness and fatigue, while the baby grows and develops rapidly. Key milestones include the formation of the baby’s fingerprints and the ability to hear sounds from outside the womb.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle during the second trimester is important, including eating a balanced diet, staying hydrated, and engaging in regular prenatal check-ups and recommended exercises. Avoid activities that pose risks to the baby, such as smoking, consuming alcohol, or participating in high-impact sports.
When does the second trimester start? The second trimester starts at week 13 of pregnancy.
Week 13 of Pregnancy
During week 13 of pregnancy, your baby is growing rapidly and developing unique features. Their fingerprints and footprints are forming, and their hair follicles are starting to develop. Their vocal cords are continuing to develop, and they are able to make small squeaking sounds. Your body is going through some changes, with your uterus growing and your breasts continuing to enlarge. You notice that your nausea and fatigue are starting to subside, and you feel more energetic and hungry.
While many women experience a decrease in symptoms when 13 weeks pregnant, some still experience them. 13 weeks pregnant symptoms include fatigue, breast tenderness, frequent urination, constipation, and heartburn. You notice some skin changes, such as darkening of the areolas or a line appearing down the center of your abdomen.
Your baby’s development is focused on growth and refinement this week. Their bones are continuing to harden, and their muscles are getting stronger. Their intestines are moving back into their abdomen from the umbilical cord, and their liver is starting to produce bile, which is important for digestion.
Week 14 of Pregnancy
Week 14 of pregnancy marks the beginning of the second trimester. Your baby, now about the size of a lemon, continues growing and developing rapidly. Their eyes move closer to the front of their head, and their ears approach their final positions. Their neck is getting longer, and they are able to turn their heads. You feel more energetic and less nauseous this week and even start to feel your baby move.
You notice that your appetite increases and you’re gaining weight. Remember to eat a healthy diet and stay active. 14 weeks pregnant symptoms include fatigue, breast tenderness, nasal congestion, bleeding gums, and leg cramps.
This week, your baby’s development is focused on growth and refinement. Their bones are continuing to harden, and their muscles are getting stronger. Their face is becoming more defined, and their skin is still very thin and transparent. Their reproductive organs are continuing to develop, and if you have an ultrasound, you will likely find out the sex of your baby.
Week 15 of Pregnancy
In week 15 of pregnancy, your baby is about the size of an apple and continues to grow and develop rapidly. Their legs are longer than their arms, and their joints are more flexible. They now make a variety of movements, such as sucking their thumb, yawning, and stretching. You feel your baby move, although it initially feels like flutters or gas bubbles.
You feel more energetic and less nauseous this week, and your appetite increases. Common 15 weeks pregnant symptoms include fatigue, breast tenderness, nasal congestion, bleeding gums, and leg cramps. You notice your skin becoming oilier or drier and develop some stretch marks.
This week, your baby’s development is focused on growth and refinement. Their skeleton is hardening, and their muscles are getting stronger. Their skin is still thin and transparent, but it’s starting to thicken. Their ears are almost in their final position, and they now hear sounds.
Week 16 of Pregnancy
Week 16 of pregnancy is exciting as your baby becomes more active and develops unique features. They are now about the size of an avocado and able to move their eyes, although their eyelids are still fused shut. Their taste buds are starting to develop, and they are able to taste the amniotic fluid. You feel your baby’s movements more clearly in week 16 of pregnancy, and you see them on an ultrasound. Your body is changing, with your uterus growing and your breasts becoming fuller.
You notice that your skin is becoming darker in certain areas, such as your nipples and a line down the center of your abdomen. Common 16 weeks pregnant symptoms include fatigue, heartburn, constipation, nasal congestion, and leg cramps.
This week, your baby’s development is focused on refining its senses and bodily systems. Its eyes are becoming more light-sensitive, and its ears continue developing. Its muscles are getting stronger, and it now makes more coordinated movements. Its blood vessels are developing, and its heart is pumping about 25 quarts of blood each day.
Week 17 of Pregnancy
Week 17 of pregnancy is a time of continued growth and development for your baby, who is now about the size of a turnip. Their skeleton is hardening, and their bones are becoming stronger. Their legs grow longer than their arms, and their bodies become more proportionate. They are starting to develop a layer of fat beneath their skin, which helps to regulate their body temperature after birth. On an ultrasound, you see your baby’s movements more regularly in week 17 of pregnancy.
You experience some round ligament pain, a sharp, stabbing pain in your lower abdomen or groin that occurs as your uterus expands. Common 17 weeks pregnant symptoms include fatigue, heartburn, constipation, nasal congestion, and leg cramps.
This week, your baby’s development is focused on growth and refinement. Their skeleton is continuing to harden, and their muscles are getting stronger. Their fat layer is developing, and their skin is becoming thicker. Their ears continue to develop, and they now hear a wider range of sounds.
Week 18 of Pregnancy
Week 18 of pregnancy is exciting as your baby becomes more active and develops their senses. They are now about the size of a bell pepper and make various movements, such as kicking, punching, and hiccupping. They hear your voice and other sounds from the outside world. You see your baby’s movements more distinctly during week 18 of pregnancy on an ultrasound.
You experience swelling in your hands and feet and notice your veins becoming more visible. Common 18 weeks pregnant symptoms include fatigue, heartburn, constipation, backache, and round ligament pain.
This week, your baby’s development is focused on refining its senses and bodily systems. Its eyes are continuing to develop, and it now blinks. Its ears continue to develop, and it now hears a wider range of sounds. Its brain is developing rapidly and starting to form connections between neurons.
Week 19 of Pregnancy
During week 19 of pregnancy, your baby continues to grow and develop rapidly. They are now about the size of a mango, and their movements are becoming stronger and more coordinated. They now suck their thumb, grasp their umbilical cord, and even yawn. They are starting to develop a sense of touch, and they are able to feel the walls of the uterus. You notice a pattern in your baby’s movements this week, and you are able to tell when they are awake or asleep.
You experience swelling in your hands and feet and develop varicose veins. Common 19 weeks pregnant symptoms include fatigue, heartburn, constipation, backache, and round ligament pain.
This week, your baby’s development is focused on growth and refinement. Their body is becoming more proportionate, and their limbs are lengthening. Their skin is becoming thicker, and a protective coating called vernix caseosa is developing. Their brain continues to develop rapidly, and they are starting to form connections between neurons.
Week 20 of Pregnancy
Week 20 of pregnancy marks the halfway point of your pregnancy. Your baby is now about the size of a banana and continues to grow and develop rapidly. They are starting to swallow amniotic fluid, which is important for their digestive system development. They are starting to produce meconium, the dark, sticky substance that is their first bowel movement after birth. You feel your baby’s movements more strongly this week and see them on an ultrasound.
You experience swelling in your hands and feet and develop varicose veins. Common 20 weeks pregnant symptoms include fatigue, heartburn, constipation, backache, and round ligament pain.
This week, your baby’s development is focused on growth and refinement. Their body is becoming more proportionate, and their limbs are lengthening. Their skin is becoming thicker and developing more layers. Their hair is growing, and their eyebrows and eyelashes are becoming more defined.
Week 21 of Pregnancy
During week 21 of pregnancy, your baby is about the size of a carrot and is becoming more active and alert. They now sense light and sound and respond to your voice or touch. They are starting to develop a sleep-wake cycle, and you notice that they are more active at certain times of the day. Your body is changing, with your uterus growing and your breasts becoming fuller.
You experience some swelling in your hands and feet and develop some stretch marks. Common 21 weeks pregnant symptoms include fatigue, heartburn, constipation, backache, and round ligament pain.
This week, your baby’s development is focused on refining its senses and bodily systems. Its eyes continue developing, and it now sees light and dark. Its ears continue to develop, and it hears a wider range of sounds. Its brain is developing rapidly, forming more complex connections between neurons.
Week 22 of Pregnancy
Week 22 of pregnancy is a time of continued growth and development for your baby, who is now about the size of a spaghetti squash. Their senses are becoming more refined, and they now taste the amniotic fluid. They start to develop a sense of smell and recognize your scent. Your body is changing, with your uterus growing and your breasts becoming fuller.
You experience some Braxton Hicks contractions, which are painless contractions that help to prepare your body for labor. Common 22 weeks pregnant symptoms include fatigue, heartburn, constipation, backache, and round ligament pain.
This week, your baby’s development is focused on growth and refinement. Their body is becoming more proportionate, and their limbs are lengthening. Their skin is becoming thicker and developing more layers. Their hair is growing, and their eyebrows and eyelashes are becoming more defined.
Week 23 of Pregnancy
During week 23 of pregnancy, your baby is about the size of a grapefruit and is starting to look more like a newborn. Their skin is still thin and wrinkled, but it’s starting to fill out with fat. Their lungs are developing, and they practice breathing movements by inhaling and exhaling amniotic fluid. You feel your baby’s movements more strongly this week and see them on an ultrasound.
Common 23 weeks pregnant symptoms include overactive bladders, lower back pain, and pregnancy brain. You experience some Braxton Hicks contractions, and you notice that your skin is becoming drier.
This week, your baby’s development is focused on growth and refinement. Their body is becoming more proportionate, and their limbs are lengthening. Their skin is becoming thicker and developing more layers. Their hair is growing, and their eyebrows and eyelashes are becoming more defined.
Week 24 of Pregnancy
Week 24 of pregnancy is an important milestone as your baby is now considered viable, meaning they are able to survive if born prematurely. They are about the size of an ear of corn, and their lungs continue to develop. They are starting to produce surfactant, which helps keep their lungs inflated after birth. You feel your baby’s movements more frequently during week 24 of pregnancy and see their hiccups on an ultrasound.
Common symptoms during this week include fatigue, heartburn, constipation, backache, and round ligament pain. Braxton Hicks contractions are 24 weeks pregnant symptoms.
This week, your baby’s development is focused on growth and refinement. Their body is becoming more proportionate, and their limbs are lengthening. Their skin is becoming thicker and developing more layers. Their hair is growing, and their eyebrows and eyelashes are becoming more defined.
Week 25 of Pregnancy
In week 25 of pregnancy, your baby is about the size of a rutabaga and continues to grow and develop rapidly. Their senses are becoming more refined, and they now taste the amniotic fluid, hear your voice, and feel your touch. They develop a sense of balance and turn their heads from side to side. You notice your baby has a favorite position in the womb, and you feel them kicking or punching.
Common symptoms include fatigue, heartburn, constipation, backache, and round ligament pain. Other common 25 weeks pregnant symptoms are Braxton Hicks contractions and dry skin.
This week, your baby’s development is focused on growth and refinement. Their body is becoming more proportionate, and their limbs are lengthening. Their skin is becoming thicker and developing more layers. Their hair is growing, and their eyebrows and eyelashes are becoming more defined.
Week 26 of Pregnancy
Week 26 of pregnancy is a time of continued growth and development for your baby, who is now about the size of a leek. Their lungs are continuing to mature, and they are starting to practice breathing movements by inhaling and exhaling amniotic fluid. Their eyes are developing, and they open and close their eyelids. You start to feel your baby’s movements more frequently during week 26 of pregnancy, and you see them hiccups on an ultrasound.
Common symptoms include fatigue, heartburn, constipation, backache, and round ligament pain. Other 26 weeks pregnant symptoms are Braxton Hicks contractions and dry skin.
This week, your baby’s development is focused on growth and refinement. Their body is becoming more proportionate, and their limbs are lengthening. Their skin is becoming thicker and developing more layers. Their hair is growing, and their eyebrows and eyelashes are becoming more defined.
Week 27 of Pregnancy
During week 27 of pregnancy, your baby is about the size of a cauliflower and continues to grow and develop rapidly. Their brain is developing rapidly, and they are forming memories and learning. They hear your voice and other sounds from the outside world and respond to them. You notice your baby has a favorite position in the womb, and you feel them kicking or punching.
Common symptoms include fatigue, heartburn, constipation, backache, and round ligament pain. 27 weeks pregnant symptoms are Braxton Hicks contractions and dry skin.
This week, your baby’s development is focused on growth and refinement. Their body is becoming more proportionate, and their limbs are lengthening. Their skin is becoming thicker and developing more layers. Their hair is growing, and their eyebrows and eyelashes are becoming more defined.
Week 28 of Pregnancy
Week 28 of pregnancy marks the beginning of the third trimester. Your baby is about the size of an eggplant and continues to grow and develop rapidly. Their lungs are almost fully developed, and they are starting to practice breathing movements more regularly. They are developing a sense of sight and now open and close their eyes. You feel your baby’s movements more frequently this week and see them hiccup or yawn on an ultrasound.
Common 28 weeks pregnant symptoms include fatigue, heartburn, constipation, backache, and round ligament pain. Other 28 weeks pregnant symptoms include Braxton Hicks contractions, and you notice that your skin is becoming drier.
This week, your baby’s development is focused on growth and refinement. Their body is becoming more proportionate, and their limbs are lengthening. Their skin is becoming thicker and developing more layers. Their hair is growing, and their eyebrows and eyelashes are becoming more defined.
Third Trimester of Pregnancy
The third trimester of pregnancy encompasses weeks 29 through 40. During the third trimester, the baby grows with the fetus gaining weight and the organs maturing in preparation for life outside the womb. Third-trimester pregnancy symptoms include a range of physical symptoms, such as increased backache, fatigue, shortness of breath, and Braxton Hicks contractions, as the growing baby puts more pressure on the mother’s body.
It is crucial to prioritize rest, maintain a healthy diet, stay well-hydrated, and attend regular prenatal check-ups during the third trimester while avoiding strenuous activities, lying flat on your back for extended periods, and consuming substances that harm the baby, such as alcohol, tobacco, and certain medications unless prescribed by a healthcare provider.
During this trimester, you mentally and physically prepare for labor. Attend childbirth education classes to learn about labor and delivery, pain management options, and coping strategies. Practice relationship techniques, get enough rest, and maintain a balanced diet to keep your body well-nourished and prepared for the physical demands of labor.
Week 29 of Pregnancy
In week 29 of pregnancy, your baby is about the size of a butternut squash and continues to grow and develop rapidly. Their bones are hardening, and their muscles are getting stronger. They are starting to develop a layer of fat beneath their skin, which helps to regulate their body temperature after birth. You feel your baby’s movements more frequently in week 29 of pregnancy, and you see them hiccups or yawn on an ultrasound. Common 29 weeks pregnant symptoms during this week include fatigue, heartburn, constipation, backache, and round ligament pain. You experience some Braxton Hicks contractions, and you notice that your skin is becoming drier or itchy.
This week, your baby’s development is focused on growth and refinement. Their body is becoming more proportionate, and their limbs are lengthening. Their skin is becoming thicker and developing more layers. Their hair is growing, and their eyebrows and eyelashes are becoming more defined. Their lungs are almost fully developed and starting to produce surfactant, which helps keep their lungs inflated after birth.
Week 30 of Pregnancy
During week 30 of pregnancy, your baby is about the size of a cabbage and continues to grow and develop rapidly. They are gaining weight quickly, and their body is becoming more rounded and plump. Their bones are hardening, and their muscles are getting stronger. They are starting to develop their immune system and receive antibodies from you through the placenta. You feel your baby’s movements more frequently and strongly during week 30 of pregnancy, and you see them hiccup or yawn on an ultrasound.
Common symptoms during this week include fatigue, heartburn, constipation, backache, and round ligament pain. Other 30 weeks pregnant symptoms include Braxton Hicks contractions. You notice that your skin is becoming drier or itchy.
This week, your baby’s development is focused on growth and refinement. Their body is becoming more proportionate, and their limbs are lengthening. Their skin is becoming thicker and developing more layers. Their hair is growing, and their eyebrows and eyelashes are becoming more defined. Their eyes are now open, and they see light and dark.
Week 31 of Pregnancy
During week 31 of pregnancy, your baby is about the size of a coconut and continues to grow and develop rapidly. They are gaining weight quickly, and their body is becoming more rounded and plump. Their bones are hardening, and their muscles are getting stronger. They are starting to develop their immune system and receive antibodies from you through the placenta. You feel your baby’s movements more frequently and strongly during week 31 of pregnancy, and you see them hiccup or yawn on an ultrasound.
Common symptoms during this week include fatigue, heartburn, constipation, backache, and round ligament pain. Other 31 weeks pregnant symptoms include Braxton Hicks contractions and dry or itchy skin.
This week, your baby’s development is focused on growth and refinement. Their body is becoming more proportionate, and their limbs are lengthening. Their skin is becoming thicker and developing more layers. Their hair is growing, and their eyebrows and eyelashes are becoming more defined. Their eyes are now open, and they see light and dark.
Week 32 of Pregnancy
Week 32 of pregnancy marks another milestone in your baby’s development. They are now about the size of a jicama and continue to grow and develop rapidly. Their lungs are almost fully developed, and they practice breathing movements more regularly. They are starting to develop their sense of sight, and they now open and close their eyes and turn their head towards light. You feel your baby’s movements more frequently this week and see them hiccup or yawn on an ultrasound.
Common symptoms during week 32 of pregnancy include fatigue, heartburn, constipation, backache, round ligament pain, Braxton Hicks contractions, shortness of breath, and swelling in the feet and ankles. You likely experience difficulty sleeping, another one of the common 32 weeks pregnant symptoms, due to discomfort and frequent urination.
Your baby’s development is focused on growth and refinement this week. Their body is becoming more proportionate, and their limbs are lengthening. Their skin is becoming smoother as they gain more fat. Their central nervous system is maturing, and they are developing reflexes like sucking and swallowing.
Week 33 of Pregnancy
During week 33 of pregnancy, your baby is about the size of a pineapple and continues to grow and develop rapidly. Their bones are hardening, and their muscles are getting stronger. They are starting to develop their immune system and receive antibodies from you through the placenta. You feel your baby’s movements more frequently and strongly this week, and you see them hiccup or yawn on an ultrasound.
Common symptoms during week 33 of pregnancy include fatigue, heartburn, constipation, backache, round ligament pain, Braxton Hicks contractions, shortness of breath, and swelling in the feet and ankles. Other common 33 weeks pregnant symptoms are difficulty sleeping due to discomfort and frequent urination.
This week, your baby’s development is focused on growth and refinement. Their body is becoming more proportionate, and their limbs are lengthening. Their skin is becoming smoother as they gain more fat. Their central nervous system is maturing, and they are developing reflexes like sucking and swallowing.
Week 34 of Pregnancy
Week 34 of pregnancy is exciting as your baby starts to get into position for birth. They are now about the size of a cantaloupe and continue to grow and develop rapidly. Their lungs are almost fully developed, and they practice breathing movements more regularly. They are starting to develop their sense of sight, and they now open and close their eyes and turn their head towards light. You feel your baby’s movements more frequently during week 34 of pregnancy, and you see them hiccup or yawn on an ultrasound.
Common symptoms during this week include fatigue, heartburn, constipation, backache, round ligament pain, Braxton Hicks contractions, shortness of breath, and swelling in the feet and ankles are among 34 weeks pregnant symptoms. Other common 34 weeks pregnant symptoms include difficulty sleeping due to discomfort and frequent urination.
Your baby’s development is focused on growth and refinement this week. Their body is becoming more proportionate, and their limbs are lengthening. Their skin becomes smoother as they gain more fat. Their central nervous system is maturing, and they are developing reflexes like sucking and swallowing.
Week 35 of Pregnancy
In week 35 of pregnancy, your baby is about the size of a honeydew melon and continues to grow and develop rapidly. Their bones are hardening, but their skull remains soft and flexible, allowing passage through the birth canal. They are starting to develop their immune system and receive antibodies from you through the placenta. You feel your baby’s movements more frequently and strongly during week 35 of pregnancy, and you see them hiccup or yawn on an ultrasound. Common 35 weeks pregnant symptoms during this week include fatigue, heartburn, constipation, backache, round ligament pain, Braxton Hicks contractions, shortness of breath, and swelling in the feet and ankles. You likely experience difficulty sleeping due to discomfort and frequent urination.
This week, your baby’s development is focused on growth and refinement. They continue to gain weight, and their organs mature. Their skin is becoming smoother and less wrinkled. Their fingernails have reached their fingertips, and their toenails are almost there.
Week 36 of Pregnancy
Week 36 of pregnancy marks another milestone as your baby approaches term. They are now about the size of romaine lettuce and continue growing and developing rapidly. Their lungs are almost fully mature, and they continue practicing breathing movements. They are starting to develop their sense of hearing and now recognize your voice and other sounds from the outside world. You feel your baby’s movements less frequently during week 36 of pregnancy as they have less space to move around in your womb. Common 36 weeks pregnant symptoms during this week include fatigue, heartburn, constipation, backache, round ligament pain, Braxton Hicks contractions, shortness of breath, and swelling in the feet and ankles. You likely experience difficulty sleeping due to discomfort and frequent urination.
This week, your baby’s development is focused on growth and refinement. They are continuing to gain weight and their organs are maturing. Their skin is becoming smoother and less wrinkled. Their fingernails have reached their fingertips, and their toenails are almost there.
Week 37 of Pregnancy
Week 37 of pregnancy marks when your baby is considered early term. Your baby is now about the size of Swiss chard and continues to grow and develop slower. Their lungs are mature, and they are ready to breathe independently. They continue developing their senses and become more capable of seeing, hearing, tasting, smelling, and touching. You feel your baby’s movements less frequently during week 37 of pregnancy as they have less space to move around in your womb. Common 37 weeks pregnant symptoms during this week include fatigue, heartburn, constipation, backache, round ligament pain, Braxton Hicks contractions, shortness of breath, and swelling in the feet and ankles. You likely experience difficulty sleeping due to discomfort and frequent urination.
This week, your baby’s development is focused on gaining weight and preparing for birth. They continue developing their reflexes and starting to position themselves for delivery. Their head starts moving down into your pelvis, known as engagement.
Week 38 of Pregnancy
Week 38 of pregnancy is exciting as your baby is almost ready to be born. They are about the size of a leek and continue to grow and develop slower. Their lungs are mature, and they are ready to breathe independently. They continue developing their senses and are able to see, hear, taste, smell, and touch. You feel your baby’s movements less frequently this week as they have less space to move around in your womb.
Common symptoms during week 38 of pregnancy include fatigue, heartburn, constipation, backache, round ligament pain, Braxton Hicks contractions, shortness of breath, and swelling in the feet and ankles. You likely experience other 38 weeks pregnant symptoms, such as difficulty sleeping due to discomfort and frequent urination.
This week, your baby’s development is focused on gaining weight and preparing for birth. They continue developing their reflexes and starting to position themselves for delivery. Their head starts moving down into your pelvis, known as engagement.
Week 39 of Pregnancy
In week 39 of pregnancy, your baby is considered full-term and is ready to be born. They are now about the size of a small watermelon and continue gaining weight but at a slower pace. Their organs are mature, and they are ready to function on their own. They continue developing their senses and are able to see, hear, taste, smell, and touch. You feel your baby’s movements less frequently this week as they have less space to move around in your womb. Common 39 weeks pregnant symptoms include fatigue, heartburn, constipation, backache, round ligament pain, Braxton Hicks contractions, shortness of breath, and swelling in the feet and ankles. You likely experience difficulty sleeping due to discomfort and frequent urination.
This week, your baby’s development is focused on gaining weight and preparing for birth. They continue developing their reflexes and starting to position themselves for delivery. Their head starts moving down into your pelvis, known as engagement.
Week 40 of Pregnancy
Week 40 of pregnancy is your official due date, but only about 5% of babies are born on their due date. Your baby is now considered full-term and is ready to be born. They are now about the size of a small pumpkin and have shed most of the lanugo, the fine hair that covers their body. They are losing the vernix caseosa, the waxy coating that protects their skin in the womb. You feel your baby’s movements less frequently this week as they have less space to move around in your womb, but you still feel them move several times a day. Common 40 weeks pregnant symptoms include fatigue, heartburn, constipation, backache, round ligament pain, Braxton Hicks contractions, shortness of breath, and swelling in the feet and ankles. You likely experience difficulty sleeping due to discomfort and frequent urination. Additionally, you notice an increase in vaginal discharge or even lose your mucus plug, which is a sign that labor is approaching.
This week, your baby is fully developed and waiting for birth. They are continuing to gain weight, and their organs are mature. Their fingernails and toenails have grown beyond their fingertips and toes, respectively. Their skull bones are not yet fused, which allows their heads to mold during delivery.
What Lifestyle Changes Must be Made During Pregnancy?
During pregnancy, several lifestyle changes are essential to ensure the health of both the mother and the developing baby. The following 14 changes primarily revolve around diet, exercise, and avoiding harmful substances.
- Eat a balanced and nutritious diet: Focus on whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and healthy fats. Ensure adequate intake of essential nutrients like folic acid, iron, and calcium, crucial for fetal development.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water to prevent dehydration and constipation.
- Avoid certain foods: Raw or undercooked meat, fish, and eggs, unpasteurized dairy products, soft cheeses, and certain types of fish high in mercury must be avoided to prevent foodborne illnesses and exposure to harmful substances.
- Limit caffeine intake: High caffeine consumption has been linked to miscarriage, according to a 2015 study, “A meta-analysis of risk of pregnancy loss and caffeine and coffee consumption during pregnancy,” published in the International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics. It’s best to limit or avoid coffee intake.
- Stay active: Regular, moderate-intensity exercise is generally safe and beneficial during pregnancy unless otherwise advised by your healthcare provider. It helps improve mood, reduce backaches and constipation, and promote better sleep.
- Choose safe activities: Walking, swimming, prenatal yoga, and low-impact aerobics are generally safe options. Avoid contact sports or activities with a high risk of falling.
- Listen to your body: Don’t overexert yourself; stop if you experience pain or discomfort.
- No alcohol: Alcohol consumption during pregnancy tends to lead to fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS) and fetal alcohol spectrum disorder (FASD), revealed in a 2017 study titled “Fetal Alcohol Syndrome and Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders,” published in the American Family Physician. It’s best to avoid it completely.
- No smoking: Smoking during pregnancy increases the risk of miscarriage, premature birth, low birth weight, and other complications.
- Avoid illicit drugs: Illicit drugs harm the developing fetus and must be avoided entirely.
- Consult your doctor about medications: Some medications are harmful during pregnancy, so it’s important to talk to your doctor about any medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements.
- Get enough sleep: Aim for at least 7-8 hours per night to support your body’s changes and energy levels.
- Manage stress: Practice relaxation techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises to manage stress, negatively impacting pregnancy.
- Attend prenatal appointments: Regular checkups with your healthcare provider are essential to monitor your health and your baby’s development and address any concerns or questions.
Is Prenatal Care Important?
Yes, prenatal care is very important for both the mother’s and baby’s health throughout pregnancy, week by week. Here are 7 reasons why prenatal care is essential.
- Early detection and prevention of complications: Regular prenatal checkups allow healthcare providers to monitor the pregnancy closely, detect any potential problems early on, and take necessary measures to prevent them from worsening. This includes identifying and managing conditions like gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and preterm labor.
- Monitoring fetal development: Prenatal care involves various screenings and tests to assess the baby’s growth and development. This helps ensure the baby grows healthily and identifies any potential developmental issues or birth defects.
- Nutritional guidance: Healthcare providers offer guidance on proper nutrition, which is essential for the baby’s development and the mother’s health. They will recommend prenatal vitamins and address any dietary concerns.
- Education and guidance: Prenatal visits provide a valuable opportunity for expecting mothers to receive education and guidance on various aspects of pregnancy, childbirth, and postpartum care. This includes information about healthy eating habits, exercise, breastfeeding, and infant care.
- Emotional well-being: Pregnancy is a time of emotional ups and downs, and prenatal care providers offer emotional support and address the mother’s concerns or anxieties. They provide resources for mental health support if needed.
- Vaccinations and Screenings: Prenatal care includes necessary vaccinations and screenings to protect the health of the mother and baby. This includes tests for genetic conditions, infectious diseases, and other health issues.
- Preparation for childbirth and postpartum: Prenatal care helps prepare expecting mothers for labor, delivery, and postpartum. This includes discussions about different birthing options, pain management techniques, and postpartum recovery.
How to Manage Your Mental Health During Pregnancy?
Maintaining good mental health during pregnancy is as crucial as physical health. To manage mental health during pregnancy, prioritize self-care, manage stress, build a support system, and educate yourself.
Here are some strategies to manage your mental well-being during this transformative time:
- Get enough sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours each night. If you experience discomfort, try using pillows for support or trying different sleep positions.
- Maintain a healthy diet: Nourish your body with balanced meals and snacks that include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Stay active: Engage in moderate-intensity exercise approved by your healthcare provider. Walking, swimming, dancing, and stretching help reduce stress and boost mood.
- Practice relaxation: Deep breathing exercises, meditation, and mindfulness help manage stress levels.
- Spend time outdoors: Nature has a calming effect, so try walking in the park or simply sitting outside.
- Talk to someone: Share your feelings and concerns with your partner, a trusted friend, a family member, a physician, a therapist, or a support group.
- Connect with other expectant mothers: Join prenatal classes, online forums, or support groups to share experiences and gain support from others who understand what you’re going through week by week during pregnancy.
- Ask for help: Don’t be afraid to ask your partner, family, or friends for help with practical tasks or emotional support.
- Seek professional help: If you experience persistent feelings of sadness, anxiety, or hopelessness, don’t hesitate to seek help from a therapist or counselor specializing in perinatal mental health.
- Learn about pregnancy and childbirth: Knowledge empowers you and reduces anxiety. Read books, attend classes, or consult reliable online resources to understand the changes happening in your body and prepare for labor and delivery.
- Understand perinatal mood and anxiety disorders (PMADs): Being aware of the signs and symptoms of PMADs helps you identify them early and seek appropriate support.
- Give yourself a break: Growing a whole human being is physically and emotionally demanding. Don’t put too much pressure on yourself. Accept that some days are easier than others.
- Engage in enjoyable activities: Make time for hobbies and activities that bring you joy and relaxation.
Taking care of your mental health during pregnancy is good for your well-being and your baby’s development. If you have any concerns about your mental health, reach out to your healthcare provider or a mental health professional for support. Don’t be scared to ask for help.